As an SEO consultant who has ventured into the world of email marketing, I have come to recognize the importance of email in lead generation. More and more people are relying on email for not jsut communication but for reaching the right people to sell their products.
Skip ahead for how to how to Check Your DMARC Settings ==>
Daniel Fazio aka the “Cold Email Wizard” has generated over $30M in revenue for himself and clients using email.
So its become paramount to ensure that the recipient receives your emails in their inbox and not merely flagged as spam or bounced by their over-zealous mail servers.
That is where DMARC, DKIM, and SPF have made a significant difference for email delivery.
These email authentication protocols are paramount to the inbox marketing that most online users and businesses use.
What is the difference between SPF, DMARC, and DKIM?
- SPF stands for sender policy framework.
- DKIM stands for DomainKeys Identified Mail.
- DMARC stands for Domain-based Message Authentication Reporting & Conformance.
These 3 mail authentication protocols work together to make your email more trustworthy and assure the email recipient that the email is coming from you and not an impostor or malware.
In fact, there are a number of studies conducted by ReturnPath, and Litmos confirmed that 60% of people have come across phishing emails during the last 6 months, and out of that 60%, just 31% of the emails they receive look like spam emails. The remaining were phishing emails actually coming from the sender’s email address who got spoofed/hacked.
What is SPF?
Sender Policy Framework (SPF) refers to a mechanism that aids domain holders in delineating the mail servers that they authorize to dash off electronic messages in their interest. The simple execution of this program allows the domain owner to publish the Sanitized for your protection (SPF) records in the DNS settings of their respective domain name to transfer the authorization data. The recipient’s mail server, upon receiving an email in question, can cross-check the validity of the SPF record to confirm whether or not the envisaged sender is authorized or confirmed.
If there’s no sign of the suspected sender in the SPF records, then it is reasonable to suspect its legitimacy and malign an email, or even more extremely decline its existence. SPF has the actual potential to cut off the origin of favoritism.
SPF will basically safeguard your email messages from being faked, and multiplying and reproducing attacks on systems.
What is DKIM?
DKIM, an acronym for DomainKeys Identified Mail, functions by appending a digital signature onto the header of a dispatched email. The creation of this signature is only possible through the use of a private key, but its authorization can be facilitated using a public key that’s publicly accessible in the originator’s DNS information.
After the recipient’s mail server successfully acquires the dispatched message, it immediately employs the public key to authenticate whether the digital signature is credible.
Ultimately, this protective measure significantly reduces the opportunities for cybercriminals to falsify email headers and further deceive the recipient(s).
What is DMARC?
The protocol called DMARC, or Domain-based Message Authentication Reporting & Conformance, helps to prevent email phishing attacks and also the pesky spoofing attacks. It allows domain owners to specify how their emails get authenticated and specify what action should happen if an email fails that authentication.
DMARC gets built on top of two existing mechanisms, those being SPF(Sender Policy Framework) and DKIM(DomainKeys Identified Mail) and does both the magic tricks.
DMARC also provides a way for ISPs to provide reports back to the senders about emails that passed and failed the authentication, which — fingers crossed — should give large-volume senders a pretty good idea of what’s going on with their mail.
Now do you want your organization to implement DMARC today? I assure you: it’s simple and you’ve almost certainly already done at least some of the work involved.
How to Check Your DMARC Settings?
There’s a free web-app called DMARC Checker that has made it possible for users to analyze and authenticate the DMARC records that belong to them.
Here’s an snippet of the report it provides:
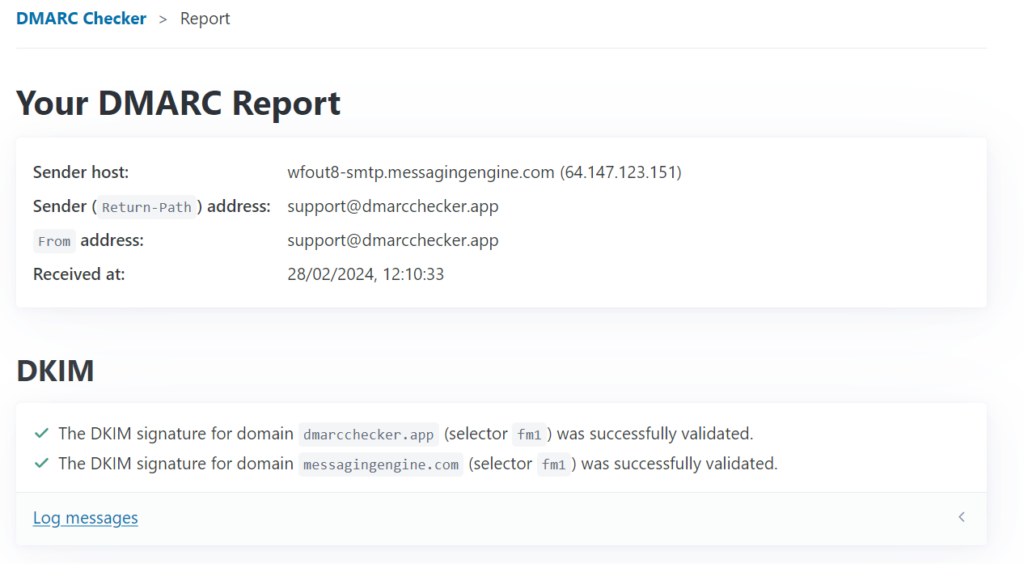
The process of examining and authenticating any DMARC record that is owned by them could not get any easier… You simply send an email to the address they list on the website and it generates a report for you, for FREE.
You’ll receive one email containing a brief overview of the check results along with a link to the complete report. Your email address will be used solely for this purpose and will not be shared with any third parties.


